Note:
This first example was made before the release of EngiLab Frame.2D 2022 (v4.0). The 2022 version introduced Units in the model. Before that the program did not support individual units directly and was working only with a consistent system of units. This example is based on this. Although the problem itself is described with specific units, these units are converted to a consistent system of units and the program works with this system. In other words, in this example we convert all quantities to equivalent quantities in a consistent units and then they are given to the program.
Another approach (using EngiLab Frame.2D 2022 or later) would be to specify the units of the problems exactly as they are given by the problem and then give quantities needed, without any conversions.
In this demonstration, we will use the consistent system of units as this specific example is compatible with version 2015 of EngiLab Frame.2D.
The first step is to define the System of Units. This is a very important step for the model. This step has nothing to do with the program itself (in versions earlier that 2022). Instead, the user has to define the preferred system of units and then all the program data have to be consistent with this system. Then the results will also comply to that system. For details, see the Consistent System of Units.
EngiLab strongly recommends the use of "EngiLab Units" for all unit conversions. EngiLab Units is a free unit conversion program that is available for download at www.engilab.com. EngiLab Units 2022 (v3.5) supports 715 units in 22 unit categories, including distance, acceleration, pressure (stress) and others. All units needed in EngiLab Frame.2D are supported by EngiLab Units.

We choose a Consistent System based on Force. We choose to use:
•m for Length (L)
•kN for Force (F)
•s for Time (T)
The derived units are then the following:
•The Acceleration unit is given by: L/T2 (1 Length unit) / (1 time unit)2. In our example: m/s2
•The Mass unit is given by: F·T2/L (1 force unit) / (1 acceleration unit). In our example: kN/(m/s2) = Mg = t (metric ton) (IMPORTANT: t has to be used instead of kg!)
•The Density unit is given by: F·T2/L4 (1 mass unit) / (1 length unit)3. In our example: t/m3 (IMPORTANT: t/m3 has to be used instead of kg/m3!)
•The Stress unit is given by: F/L2 (1 force unit) / (1 length unit)2. In our example: kN/m2
Note: The mass unit (in our example 1 t) is the mass that accelerates by the acceleration unit rate (in our example 1 m/s2) when the unit force (in our example 1 kN) is exerted on it.
The Material properties should be given as:
•E = 29 GPa = 29000000 kN/m2
•d = 2500 kg/m3 = 2.5 t/m3
The Section properties should be given as:
•Columns: Square section, 50 cm * 50 cm = 0.50 m * 0.50 m
•Beams: Rectangular section, 50 cm * 25 cm = 0.50 m * 0.25 m
The gravity acceleration should be given as g = 9.81 m/s2
In EngiLab Frame.2D before 2022 (v4.0), there are no units so there is nothing to define in the program as the Consistent System of Units is always used.
In EngiLab Frame.2D 2022 and later, we need to define the System of Units that we use, among many options. For this example, we will use the Consistent System, as follows:
Click ![]() to define the System of Units. In this example, we will use the Consistent System of units. For details, see Units
to define the System of Units. In this example, we will use the Consistent System of units. For details, see Units
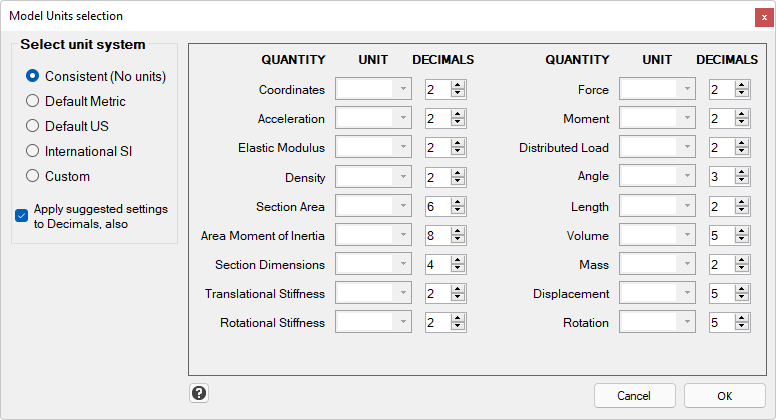
Select the Consistent System of Units. Click OK.