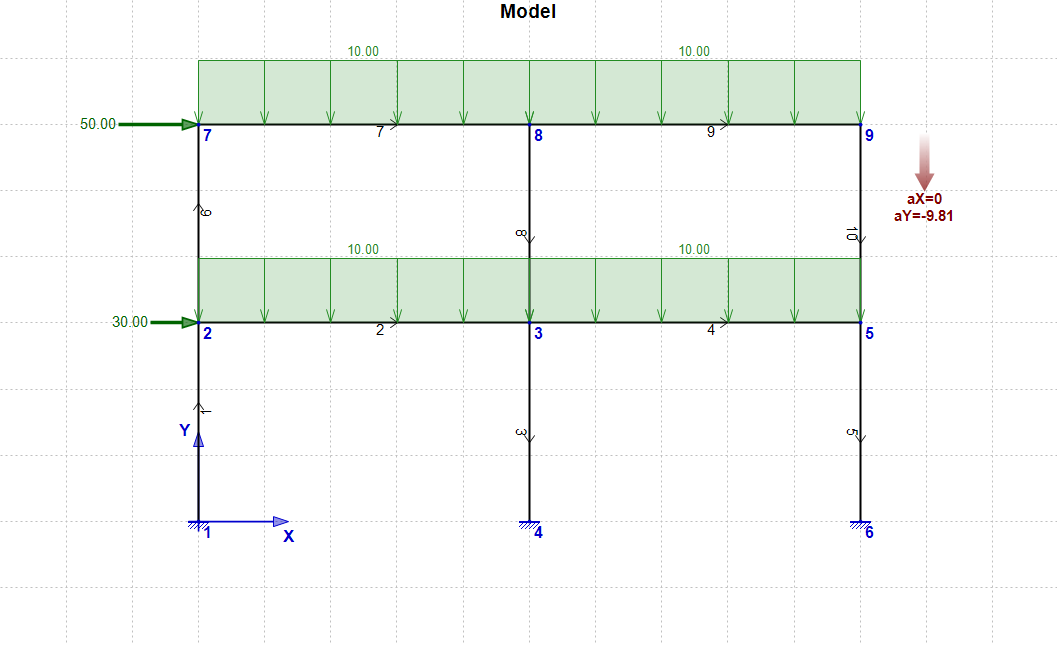
The first example is a two-story, two-bay concrete frame which is shown in the figure below.
The properties of the Model are the following:
Materials
The material of the Model is Concrete with the following properties:
•Elastic Modulus E = 29 GPa
•Density d = 2500 kg/m3
Sections
There are different sections for the Columns and Beams:
Columns: Square section, 50 cm * 50 cm
Beams: Rectangular section, 50 cm * 25 cm (bending in the major axis, i.e. 50 cm is the height of the beam (along the Global Y axis) and 25 cm is its width (perpendicular to the screen))
Member geometry (Nodes and Elements)
The geometry of the structure is as shown in the figure above, where the Grid is 1 m x 1 m. So the height of each floor is 3 m and each bay has a span of 5 m. The total height of the structure is 6 m, while the total width is 10 m.
Elements' orientation is also shown in the figure. Even if the orientation of the Elements is different, the analysis results will not change.
Nodal Loads
There is a FX=30 kN Load acting on Node 2 and also a FX=50 kN Load acting on Node 7, as shown in the figure above.
Elemental Loads
All the beams have a uniform elemental load of 10 kN/m at the direction -Y (Global axes), as shown in the figure.
Body (Acceleration) Loads
The self-weight of all the structural elements (columns and beams) has to be taken into consideration in the analysis.
The earth gravitational acceleration is given equal to g=9.81 m/s2 (a typical value).