About 2D Frames
EngiLab Frame.2D specializes in the analysis of 2D Frames. In EngiLab Frame.2D, each Node has 3 Degrees Of Freedom (DOFs), the DX-Displacement, the DY-Displacement and the RZ-Rotation. The figure below explains this and highlights the differences between EngiLab Frame.2D and EngiLab Truss.2D programs.
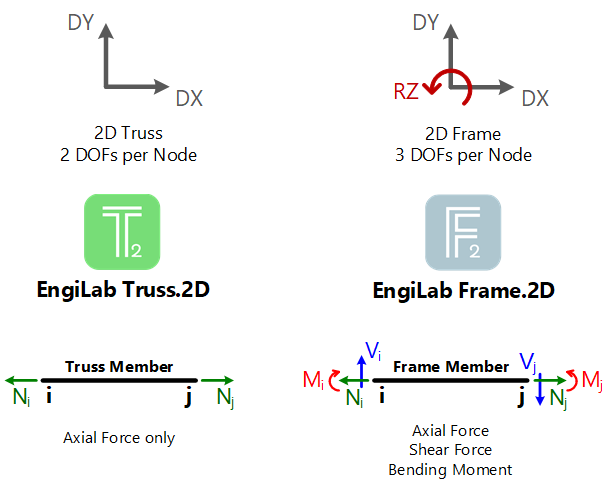
Frames are very common in engineering. A Frame in EngiLab Frame.2D has the following properties:
•All members (Elements) are straight, connecting two Nodes.
•Members are connected only at the ends of the members. If two Elements share a common Node, they are connected through this Node.
•Members can have internal hinges at either of their ends (Start i and End j). A hinge is a pin joint which means that moment will be zero at that point for the particular member.
•A member has Axial Force, Shear Force and Bending Moment, at any of its points along its length.
•Point Loads are always Nodal Loads. Nodal Loads can include FX-Force, FY-Force and MZ-Moment.
•Along an Element, there can be distributed load in the form of a uniform load or a linear varying load.