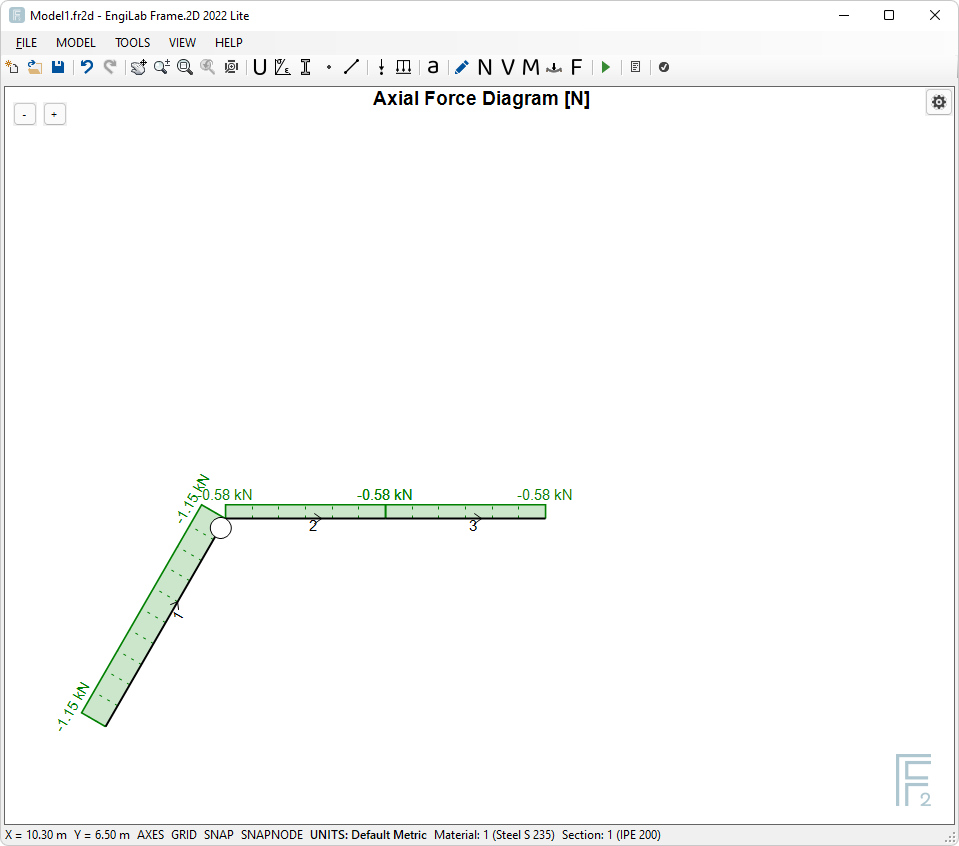
1. Axial Force Diagram
Click ![]() , to see the Axial Force Diagram. You may take the picture below.
, to see the Axial Force Diagram. You may take the picture below.
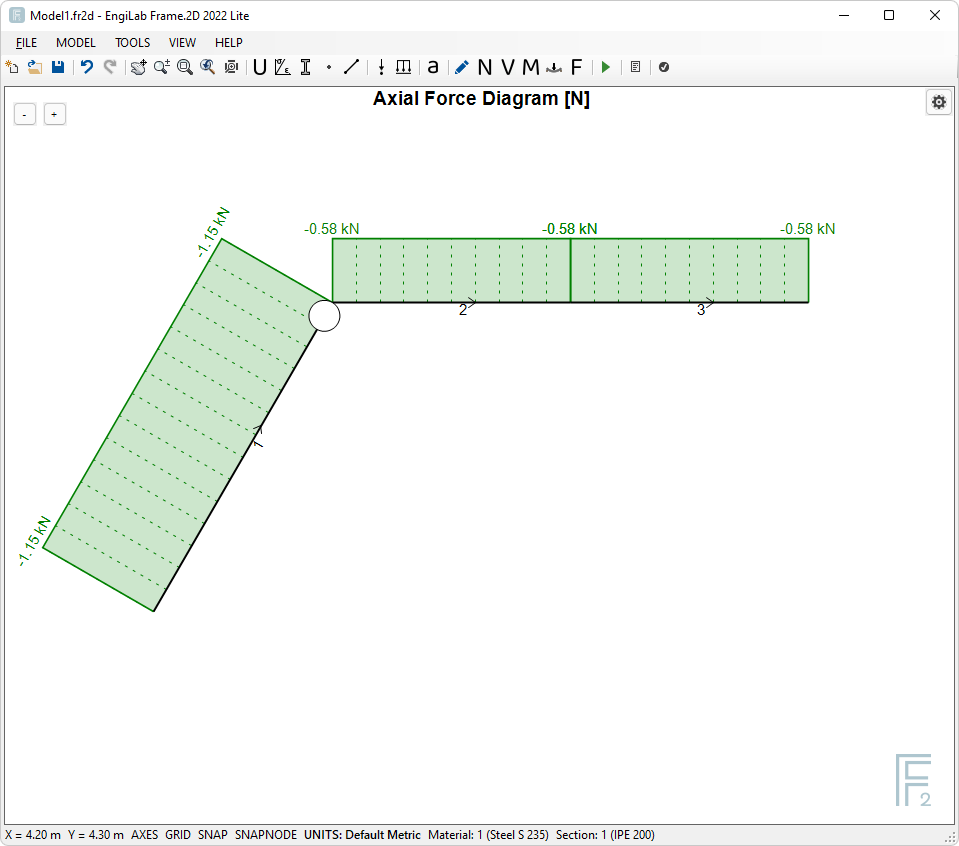
The Axial Force Diagram is out of Scale. Click the "Zoom All" button ![]() to automatically scale the Diagram.
to automatically scale the Diagram.
Now the result should look like this, which is much better.
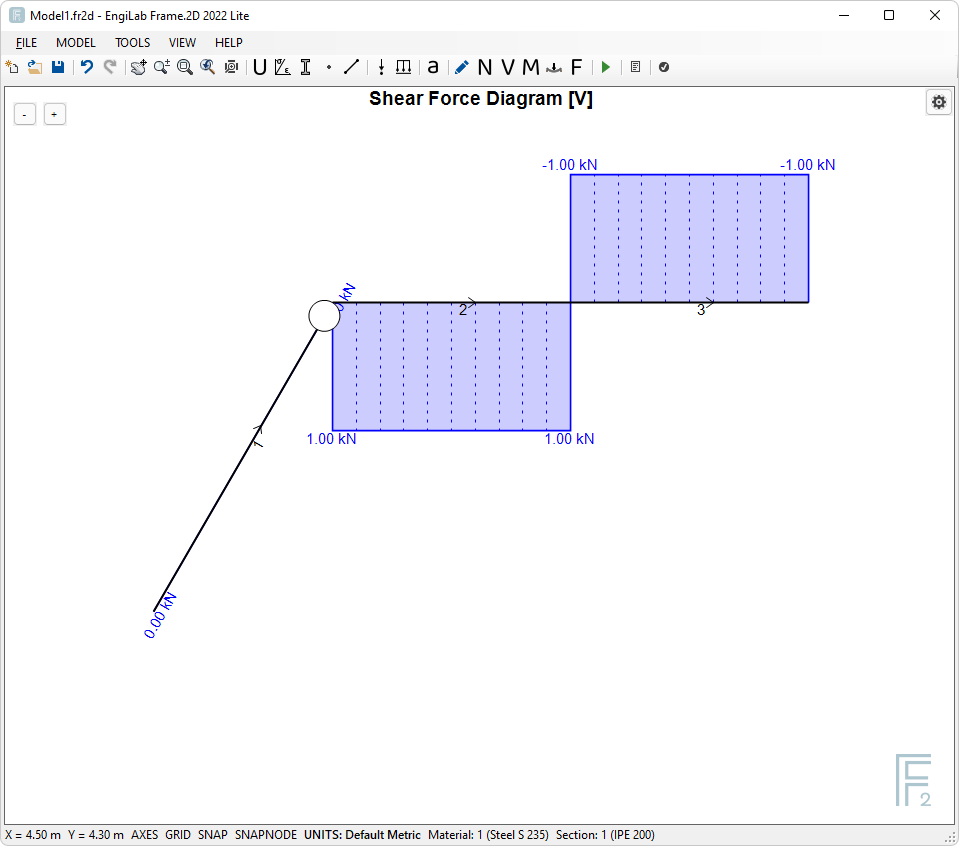
2. Shear Force Diagram
Click ![]() , to see the Shear Force Diagram. If the Shear Force Diagram is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button
, to see the Shear Force Diagram. If the Shear Force Diagram is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button ![]() to automatically scale the Diagram. You should take the following picture.
to automatically scale the Diagram. You should take the following picture.
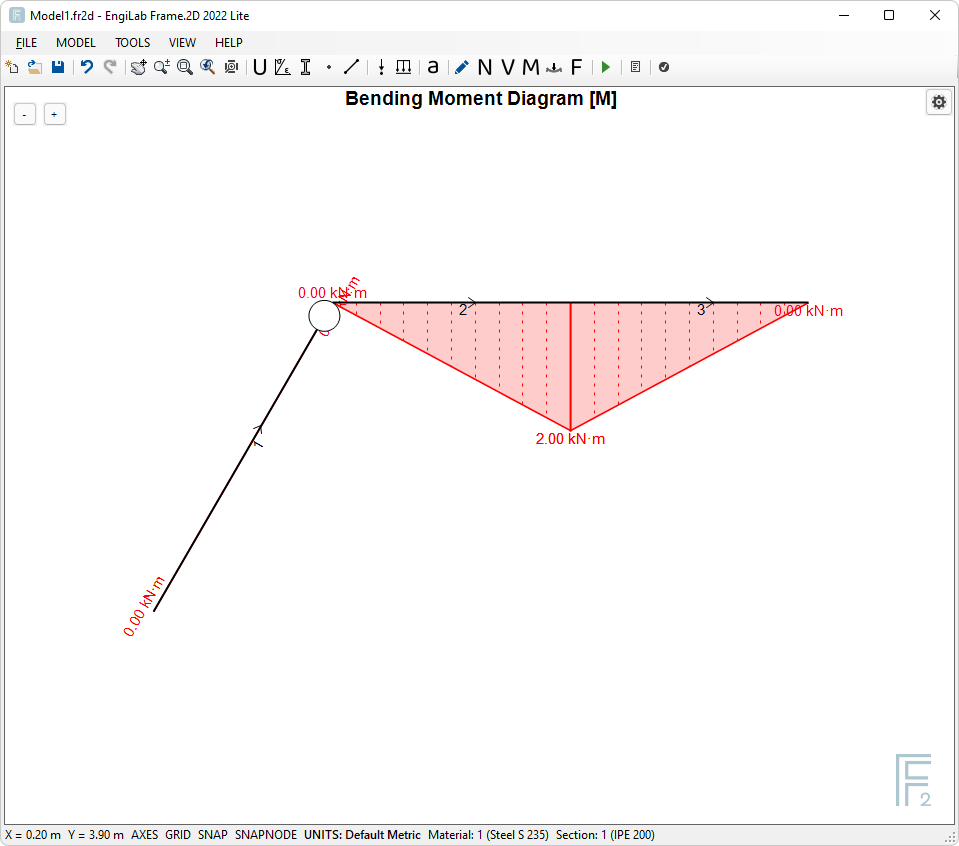
3. Bending Moment Diagram
Click ![]() , to see the Bending Moment Diagram. If the Bending Moment Diagram is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button
, to see the Bending Moment Diagram. If the Bending Moment Diagram is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button ![]() to automatically scale the Diagram. You should take the following picture.
to automatically scale the Diagram. You should take the following picture.
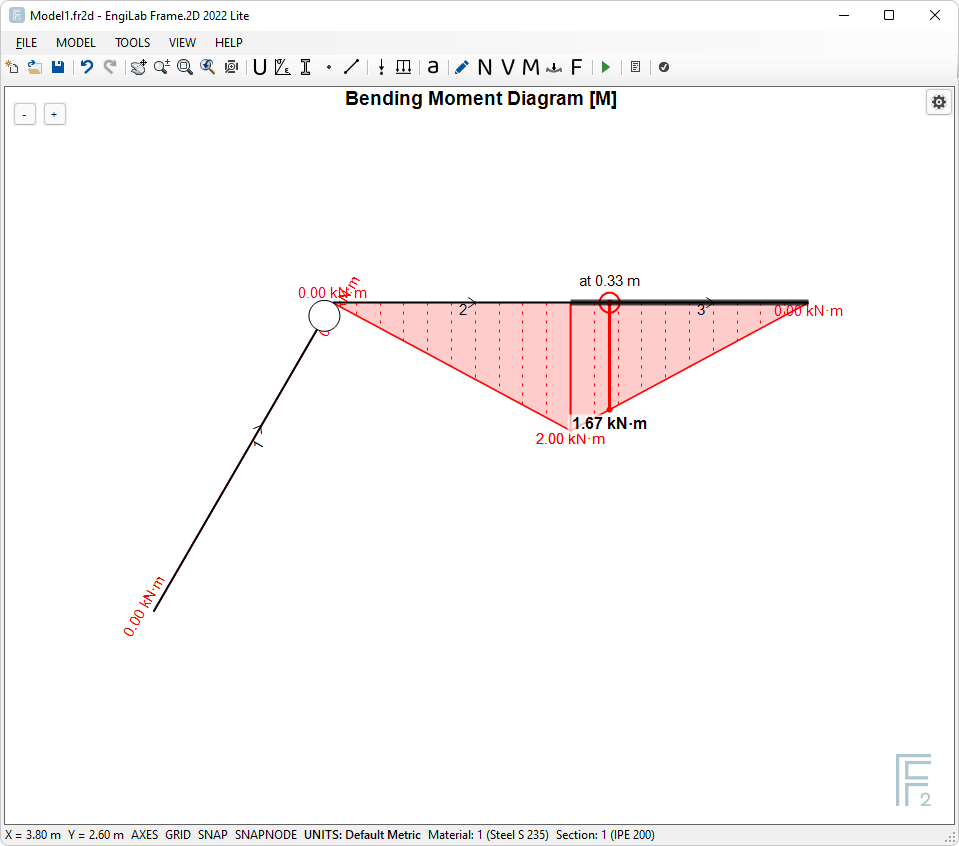
Note that if you move the pointer over an Element, you can read the corresponding value of the Diagram, as shown below for the Bending Moment Diagram case. This happens for all Diagrams and also for the Deformation and the Free Body Diagram.
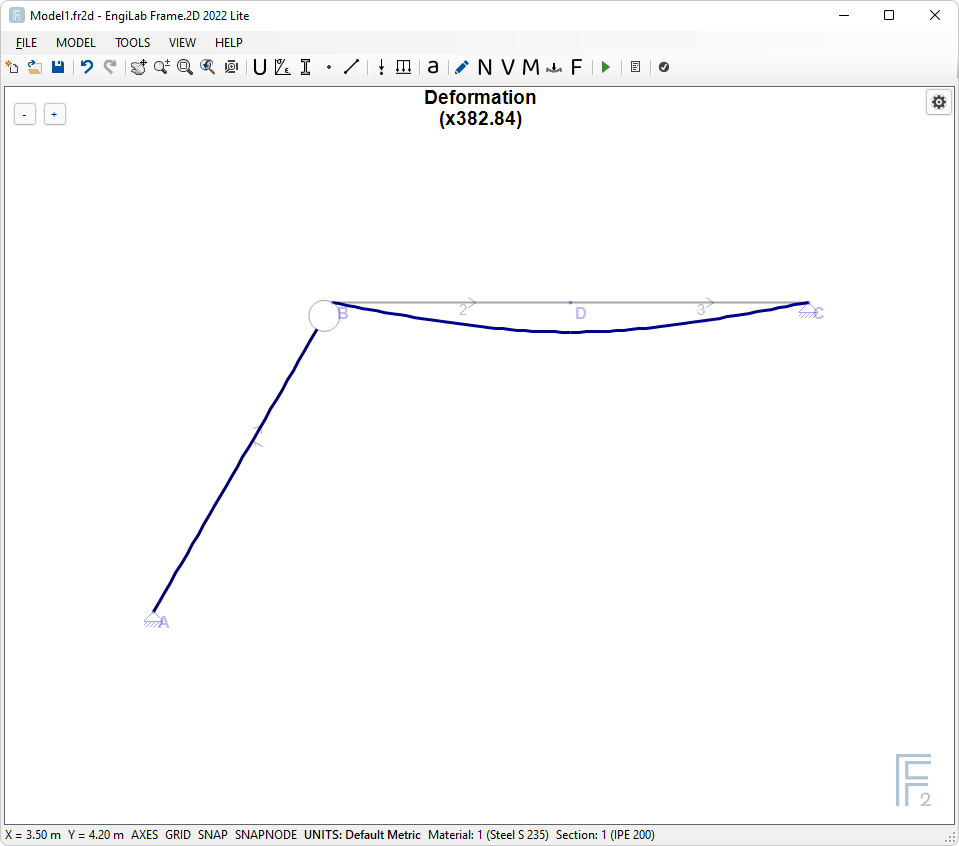
4. Deformation
Click ![]() , to see the Model Deformation. If the Deformation is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button to automatically scale it. You should take the following picture. The program reports also the Deformation magnification, in our example x382.84.
, to see the Model Deformation. If the Deformation is out of Scale, Click the "Zoom All" button to automatically scale it. You should take the following picture. The program reports also the Deformation magnification, in our example x382.84.
You can adjust scaling yourself by using the +/- buttons at the top left of the picture. If you click the "+" button a few times, you may get a picture like the one below where the magnification factor is now x957.10.
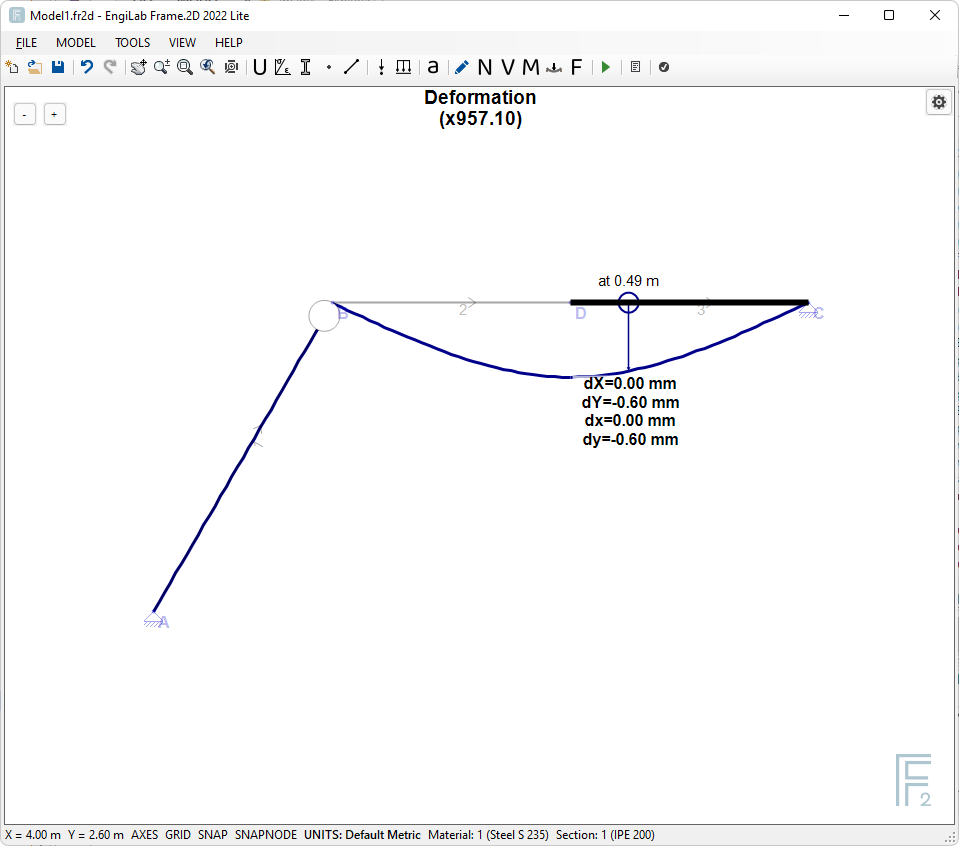
See above that you can get the deformation values on screen, if the mouse pointer hovers on an element.
IMPORTANT: The values that are given on screen are the dX, dY, dx and dy displacements of the corresponding point of each element.
•dX and dY are the X- and Y- displacements of a point, respectively, in Global axes. For example a positive dX means displacement to the right, while a positive dY means displacement upwards.
•dx and dy are the x- and y- displacements of a point, respectively, in Local Element Axes, where x is defined from the Start Node i and the End Node j of the Element and y is perpendicular to it.
5. Free Body Diagram (F)
Click ![]() , to see the Free Body Diagram of the Model. The Free Body Diagram shows the support reactions on screen and also the calculations of the equilibrium of the Model.
, to see the Free Body Diagram of the Model. The Free Body Diagram shows the support reactions on screen and also the calculations of the equilibrium of the Model.
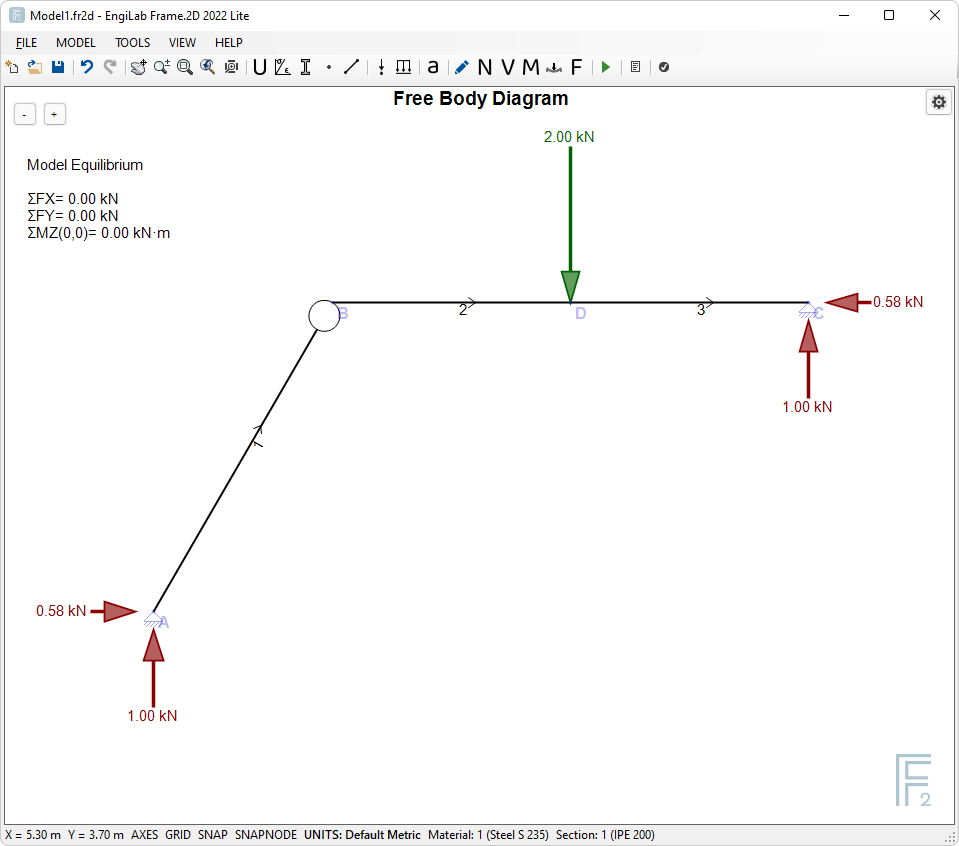
Click ![]() , to see the Free Body Diagram of the Model. The Free Body Diagram shows the support reactions on screen and also the calculations of the equilibrium of the Model.
, to see the Free Body Diagram of the Model. The Free Body Diagram shows the support reactions on screen and also the calculations of the equilibrium of the Model.
We see that the support reactions are the same as the ones found with Hand Calculations. Based on the hand calculations, the reaction forces were:
•Cx = 577 N = 0.578 kN
•Cy = 1000 N = 1 kN
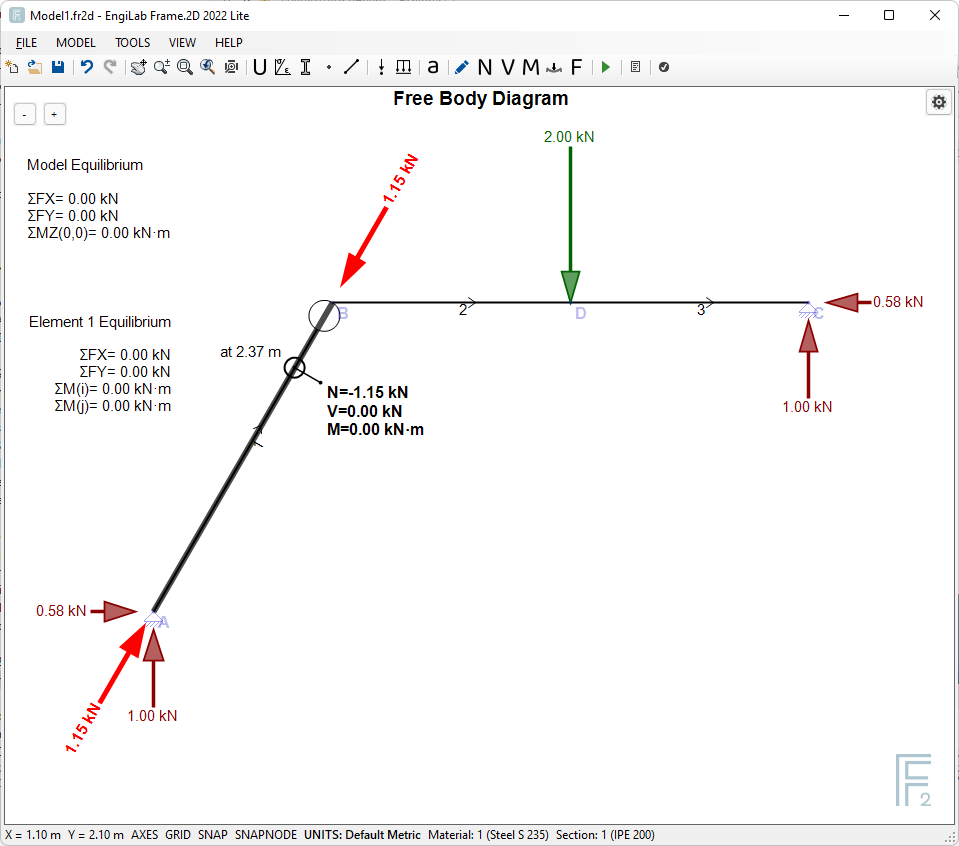
Note that if you move the pointer over an Element, you can read the corresponding N, V, M values, as shown below. The Element End Forces are also given on screen, for the specific Element and also the calculation of the equilibrium of the specific Element. For example we see that Element 1 has only axial tension:
While Element 2 has Axial Force, Shear Force and Bending Moment. There is no bending moment on the left edge (at Node B), because of the internal hinge.
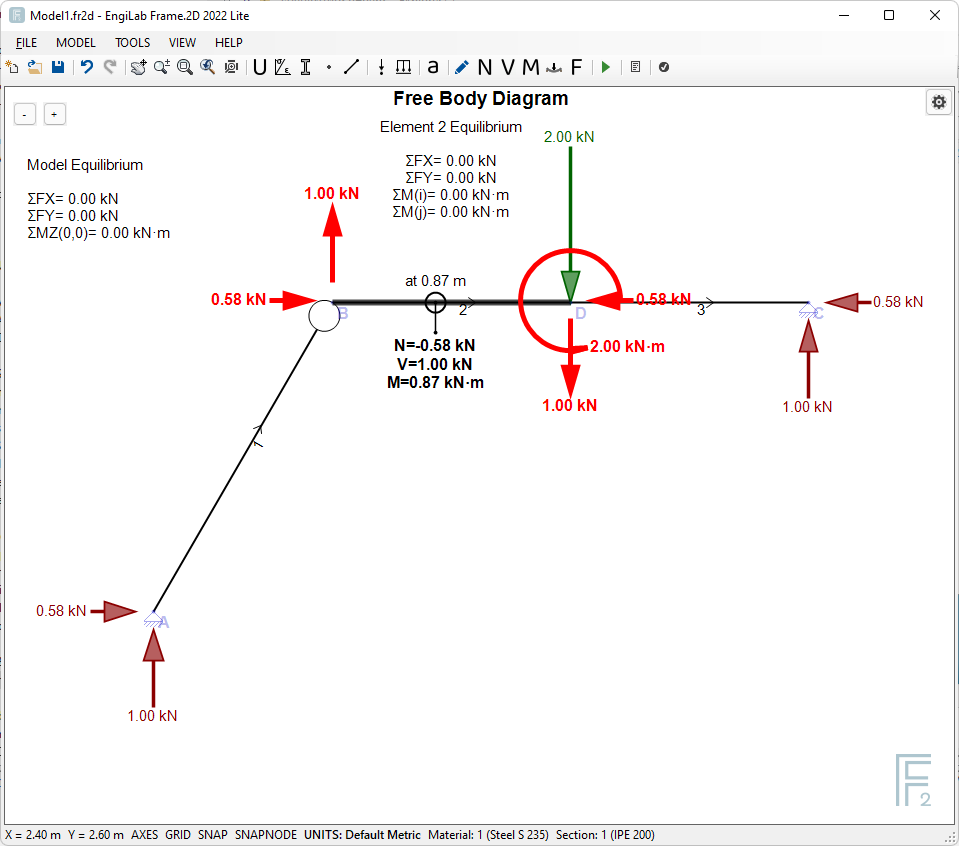
IMPORTANT: In the example above, we see the calculations of the equilibrium of Elements 1 and 2 of the Model. All equilibrium calculations (ΣFX, ΣFY, ΣM(i), ΣM(j)) are zero, otherwise there would be a problem in our Model or in the analysis results.