The following 42 Units are included in this category:
ID |
Unit (symbol) |
Definition |
Wikipedia page and other notes |
1 |
pascal (Pa) |
- |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) The same as newton per sq. metre |
2 |
newton per sq. metre (N/m2) |
1 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) The same as pascal |
3 |
newton per sq. centimetre (N/cm2) |
104 Pa |
|
4 |
newton per sq. millimetre (N/mm2) |
106 Pa |
|
5 |
hectopascal (hPa) |
102 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
6 |
kilopascal (kPa) |
103 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
7 |
kilonewton per sq. metre (kN/m2) |
103 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
8 |
kilonewton per sq. centimetre (kN/cm2) |
107 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
9 |
kilonewton per sq. millimetre (kN/mm2) |
109 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
10 |
megapascal (MPa) |
106 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
11 |
meganewton per sq. metre (MN/m2) |
106 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
12 |
gigapascal (GPa) |
109 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
13 |
giganewton per sq. metre (GN/m2) |
109 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pascal_(unit) Page refers to pascal |
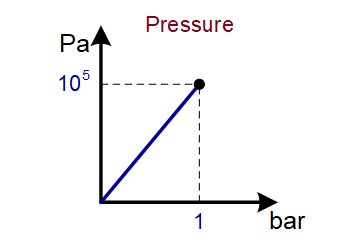
14 |
bar (bar) |
105 Pa |
|
15 |
kilobar (kbar) |
108 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(unit) Page refers to bar |
16 |
megabar (Mbar) |
1011 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(unit) Page refers to bar |
17 |
gigabar (Gbar) |
1014 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(unit) Page refers to bar |
18 |
millibar (mbar) |
102 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(unit) Page refers to bar |
19 |
microbar (μbar) |
10-1 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(unit) Page refers to bar |
20 |
pound-force per sq. inch (psi) |
(444,822,161.52605/64,516) Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pounds_per_square_inch The same as lbf/in2 |
21 |
pound-force per sq. foot (psf) |
(1/144) psi |
|
22 |
kilopound-force per sq. inch (ksi) |
103 psi |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pounds_per_square_inch#Multiples |
23 |
kilopound-force per sq. foot (ksf) |
(103/144) psi |
|
24 |
megapound-force per sq. inch (Mpsi) |
106 psi |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pounds_per_square_inch#Multiples |
25 |
megapound-force per sq. foot (Mpsf) |
(106/144) psi |
|
26 |
millimetre of mercury [conv.] (mmHg) |
133.322387415 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Millimeter_of_mercury Conventionally, the density 13,595.1 kg/m3 is used for mercury for this definition, which is the approximate density of mercury at 0 °C (32 °F), and 9.80665 m/s2 is standard gravity: 13595.1*9.80665 = 133,322.387415 for 1 metre of mercury
|
27 |
centimetre of mercury [conv.] (cmHg) |
1333.22387415 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Millimeter_of_mercury Page refers to “Millimeter of mercury” |
28 |
inch of mercury [conv.] (inHg) |
3386.388640341 Pa |
|
29 |
foot of mercury [conv.] (ftHg) |
40,636.663684092 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inch_of_mercury |
30 |
millimetre of water [conv.] (mmAq) |
9.80665 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Millimeters,_water_gauge Conventionally, the density 1,000 kg/m3 is used for water for this definition, which is the approximate density of water at 4 °C (39.2 °F), and 9.80665 m/s2 is standard gravity: 1000*9.80665 = 9806.65 for 1 metre of water Note: The maximum density of water is 999.972 kg/m3 at a temperature of 3.98 °C (39.164 °F) but conventionally we use a value of 1000 kg/m3 for water for the definition of this unit |
31 |
centimetre of water [conv.] (cmAq) |
98.0665 Pa |
|
32 |
inch of water [conv.] (inAq) |
249.08891 Pa |
|
33 |
foot of water [conv.] (ftAq) |
2989.06692 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inch_of_water Page refers to inch of water |
34 |
atmosphere [standard] (atm) |
101,325 Pa |
|
35 |
kilogram-f per sq. metre (kgf/m2) |
9.80665 Pa |
|
36 |
kilogram-f per sq. cm (kgf/cm2) |
98,066.5 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilogram-force_per_square_centimetre The same as “Technical atmosphere” |
37 |
atmosphere [technical] (at) |
98,066.5 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Technical_atmosphere The same as “kilogram-f per sq. cm” |
38 |
torr (Torr) |
(1/760) atm |
|
39 |
dyne per sq. metre (dyn/m2) |
10-5 Pa |
|
40 |
dyne per sq. centimetre (dyn/cm2) |
10-1 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barye The same as “barye” |
41 |
barye (Ba) |
10-1 Pa |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barye The same as “dyne per sq. centimetre” |
42 |
pièze (pz) |
103 Pa |
All the above definitions of the various units are EXACT.
Note that for the units based on mercury (millimetre of mercury [conv.] (mmHg), centimetre of mercury [conv.] (cmHg), inch of mercury [conv.] (inHg), foot of mercury [conv.] (ftHg)) and the units based on water (millimetre of water [conv.] (mmAq), centimetre of water [conv.] (cmAq), inch of water [conv.] (inAq), foot of water [conv.] (ftAq)), other similar definitions can be found in the literature, referring to different base temperatures, as the density of the material depends on its temperature. In the above we have used the conventional values that can be found in the literature.
Note: In the above, a period (.) is used to indicate the decimal place and a comma (,) is used to separate groups of thousands.
Type of conversion relationship: DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL (y=a∙x)
Example conversion diagram (see two units in bold above):