The following 65 Units are included in this category:
ID |
Unit (symbol) |
Definition |
Wikipedia page and other notes |
1 |
joule (J) |
- |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule Equivalent to watt second, and newton metre |
2 |
kilojoule (kJ) |
103 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule#Kilojoule Equivalent to kilowatt second |
3 |
megajoule (MJ) |
106 J |
|
4 |
gigajoule (GJ) |
109 J |
|
5 |
terajoule (TJ) |
1012 J |
|
6 |
petajoule (PJ) |
1015 J |
|
7 |
millijoule (mJ) |
10-3 J |
|
8 |
microjoule (µJ) |
10-6 J |
|
9 |
nanojoule (nJ) |
10-9 J |
|
10 |
picojoule (pJ) |
10-12 J |
|
11 |
femtojoule (fJ) |
10-15 J |
|
12 |
erg (erg) |
10-7 J |
|
13 |
pound-force inch (lbf·in) |
0.1129848290276167 J |
|
14 |
pound-force foot (lbf·ft) |
12 lbf·in |
|
15 |
ounce-force inch (ozf·in)
|
0.00706155181422604375 J |
|
16 |
ounce-force foot (ozf·ft) |
12 ozf·in |
|
17 |
watt hour (W·h) |
3600 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilowatt_hour#Watt_hour_multiples_and_billing_units |
18 |
watt second (W·s) |
1 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watt_second Equivalent to Joule and newton metre |
19 |
kilowatt second (kW·s) |
103 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watt_second Page refers to watt second Equivalent to kilojoule |
20 |
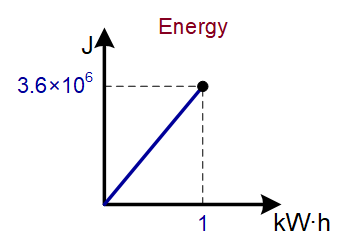
kilowatt hour (kW·h) |
3.6×106 J |
|
21 |
megawatt hour (MW·h) |
3.6×109 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilowatt_hour#Watt_hour_multiples_and_billing_units |
22 |
gigawatt hour (GW·h) |
3.6×1012 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilowatt_hour#Watt_hour_multiples_and_billing_units |
23 |
terawatt hour (TW·h) |
3.6×1015 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilowatt_hour#Watt_hour_multiples_and_billing_units |
24 |
petawatt hour (PW·h) |
3.6×1018 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kilowatt_hour#Watt_hour_multiples_and_billing_units |
25 |
milliwatt hour (mW·h) |
3.6 J |
|
26 |
microwatt hour (μW·h) |
3.6×10-3 J |
|
27 |
newton metre (N·m) |
1 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_metre Equivalent to Joule and watt second |
28 |
newton centimetre (N·cm) |
10-2 J |
|
29 |
newton millimetre (N·mm) |
10-3 J |
|
30 |
dyne metre (dyn·m) |
10-5 J |
|
31 |
dyne centimetre (dyn·cm) |
10-7 J |
|
32 |
dyne millimetre (dyn·mm) |
10-8 J |
|
33 |
kilopond metre (kp·m) |
9.80665 J |
The same as “kilogram-force metre” |
34 |
kilopond centimetre (kp·cm) |
9.80665×10-2 J |
The same as “kilogram-force centimetre” |
35 |
kilopond millimetre (kp·mm) |
9.80665×10-3 J |
The same as “kilogram-force millimetre” |
36 |
kilogram-force metre (kgf·m) |
9.80665 J |
The same as “kilopond metre” |
37 |
kilogram-force centimetre (kgf·cm) |
9.80665×10-2 J |
The same as “kilopond centimetre” |
38 |
kilogram-force millimetre (kgf·mm) |
9.80665×10-3 J |
The same as “kilopond millimetre” |
39 |
gram-force metre (gf·m) |
9.80665×10-3 J |
|
40 |
gram-force centimetre (gf·cm) |
9.80665×10-5 J |
|
41 |
gram-force millimetre (gf·mm) |
9.80665×10-6 J |
|
42 |
poundal inch (pdl·in) |
0.0035116758411504 J |
|
43 |
poundal foot (pdl·ft) |
12 pdl·in |
|
44 |
foe (foe) |
1044 J |
|
45 |
calorie [IT] (cal_IT) |
4.1868 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie The Fifth International Conference on the Properties of Steam (London, July 1956) defined the International Table calorie as exactly 4.1868 J |
46 |
calorie [Thermochemical TH] (cal_TH) |
4.184 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie It is defined as 4.184 J exactly |
47 |
calorie [15 °C] (cal15) |
4.1855 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie Can be considered an approximate definition It is the amount of energy required to warm one gram of air-free water from 14.5 to 15.5 °C at standard atmospheric pressure. Experimental values of this calorie ranged from 4.1852 to 4.1858 J. The CIPM in 1950 (Comité international des poids et mesures (International Committee for Weights and Measures) 1950; PV, 1950, 22, 79–80) published a mean experimental value of 4.1855 J, noting an uncertainty of 0.0005 J. |
48 |
kilocalorie [IT] (kcal_IT) |
4,186.8 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie Page referes to Calorie |
49 |
kilocalorie [Thermochemical TH] (kcal_TH) |
4,184 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie Page referes to Calorie |
50 |
kilocalorie [15 °C] (kcal15) |
4,185.5 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calorie Page refers to Calorie Can be considered an approximate definition, see cal15 above |
51 |
BTU [IT] (BTU_IT) |
1055.05585262 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_thermal_unit Can be considered an approximate definition The most widespread BTU uses the International Steam Table (IT) calorie, which was defined by the Fifth International Conference on the Properties of Steam (London, July 1956) to be exactly 4.1868 J. Therefore, the exact conversion factor for the International Table Btu is 1055.05585262 J, as shown in the calculation: OneLbmEqualsKg * 1000 * 5 / 9 * OneCalITEqualsJoules = 0.45359237 * 1000 * 5 / 9 * 4.1868 = 1055.05585262 |
52 |
BTU [Thermochemical TH] (BTU_TH) |
9489.1523804 / 9 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_thermal_unit Can be considered an approximate definition It is based on the definition of the thermochemical calorie, which is equal to 4.184 J. The calculation is similar to the one for the IT case: OneLbmEqualsKg * 1000 * 5 / 9 * OneCalTHEqualsJoules = 0.45359237 * 1000 * 5 / 9 * 4.184 = 9,489.1523804 / 9 ≈ 1054.35026448889 |
53 |
BTU [US, 59 °F (15 °C)] (BTU_US_59F) |
1,054.804 J |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_thermal_unit Can be considered an approximate definition 59 °F (15 °C) is the most widely used reference temperature for BTU definition in the US. Different values can be found in the literature. This value is the one most commonly used. See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_thermal_unit (reporting 1054.80 J) https://physics.nist.gov/cuu/pdf/sp811.pdf (reporting 1054.80 J) |
54 |
therm [IT] (thm_IT) |
105 BTU [IT] |
|
55 |
therm [TH] (thm_TH) |
105 BTU [Thermochemical TH] |
|
56 |
therm [US, 59 °F (15.0 °C)] (thm_US_59F) |
105 BTU [US, 59 °F (15 °C)] |
|
57 |
ton of TNT (t_TNT) |
109 cal_TH |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ton#Units_of_energy_and_power Based on that: 1 ton TNT ≈ 109 thermochemical calories Can be considered an approximate definition |
58 |
kiloton of TNT (kt_TNT) |
1012 cal_TH |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ton#Units_of_energy_and_power Based on that: 1 ton TNT ≈ 109 thermochemical calories Can be considered an approximate definition |
59 |
megaton of TNT (Mt_TNT) |
1015 cal_TH |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ton#Units_of_energy_and_power Based on that: 1 ton TNT ≈ 109 thermochemical calories Can be considered an approximate definition |
60 |
electronvolt (eV) |
1.602176634×10-19 J |
|
61 |
millielectronvolt (meV) |
10-3 eV |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronvolt Page referes to electronvolt |
62 |
kiloelectronvolt (meV) |
103 eV |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronvolt Page referes to electronvolt |
63 |
megaelectronvolt (MeV) |
106 eV |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronvolt Page referes to electronvolt |
64 |
gigaelectronvolt (GeV) |
109 eV |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronvolt Page referes to electronvolt |
65 |
teraelectronvolt (TeV) |
1012 eV |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronvolt Page referes to electronvolt |
Most of the above definitions of the various units are EXACT with the exception of the cases that are highlighted in red color.
Note: In the above, a period (.) is used to indicate the decimal place and a comma (,) is used to separate groups of thousands.
Type of conversion relationship: DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL (y=a∙x)
Example conversion diagram (see two units in bold above):